Affinity Biologicals提供了一些通用的方法,可用于建立您自己的三明治式酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA),免疫印迹或蛋白质印迹,vWF的免疫印迹和vWF的免疫组织化学。
夹心式酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)通用方案
原理:
血浆和其他液体中的分析物可以通过捕获在包被有捕获抗体的微量滴定板上进行测量。在洗涤板以去除未结合的蛋白质之后,通过与包含报告分子的另一种抗体(在这种情况下为辣根过氧化物酶)一起孵育来检测捕获的分析物。洗去未结合的检测抗体,并用过氧化物酶底物溶液显影板,产生有色的终产物。在固定的时间后,停止反应并确定微量滴定板中每个孔的吸附度。由于捕获抗体和检测抗体的浓度是固定的,因此生成的颜色与样品中存在的分析物的浓度成正比。
所需但未提供的材料:
Procedure:

References:
Nix,B, Wild D, in Immunoassays, A Practical Approach, editor J.P. Gosling, pp. 239-261, Oxford University Press, 2000.
NCCLS. Evaluation of the Linearity of Quantitative Analytical Methods; Proposed Guidline – Second Edition. NCCLS Document EP6-P2 (ISBN 1-56238-446-5, NCCLS, Wayne, Pennsylvania USA, 2001
FDA Guidance for Industry. Bioanalytical Method Validation; May 2001, available on the internet: www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM070107.pdf
Methods for Immunoblotting or Western Blotting
Immuno-Blotting (Western Blotting): Enhanced Chemiluminescent Detection using Peroxidase Labelled Primary Antibody Conjugate
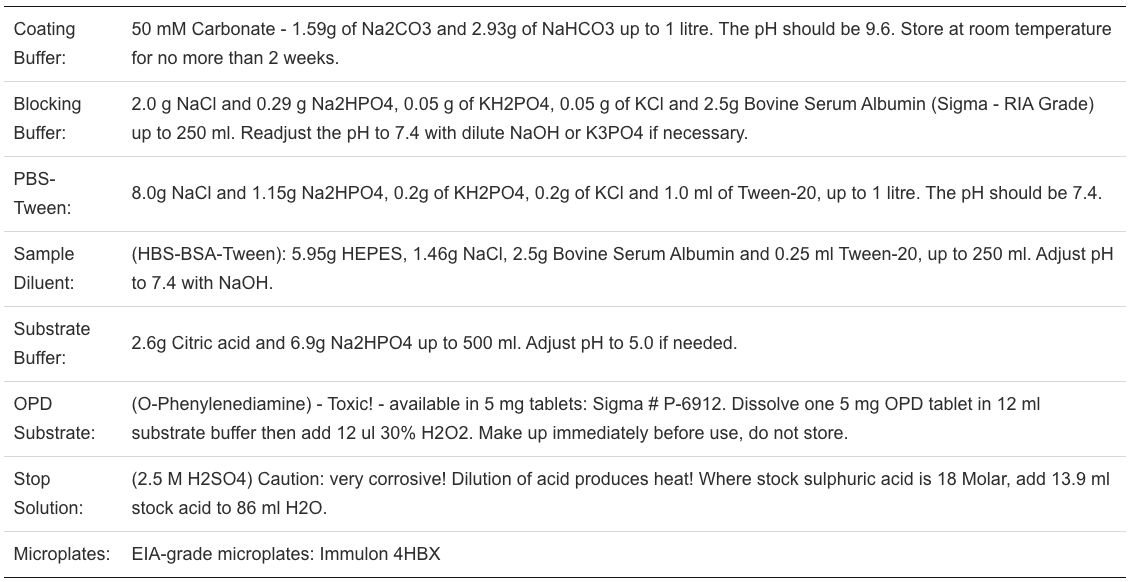
Solutions Required:
Electroblot Transfer Buffer: 0.025M Tris, 0.192M Glycine, 20% (v/v) Methanol, pH 8.3. Add 18.2 g Tris, 86.4 g Glycine, 1200 ml Methanol, up to a total volume of 6 litres.
PBS: 8.0g NaCl and 1.15g Na2HPO4, 0.2g of KH2PO4, and 0.2g of KCl, up to 1 litre. Adjust pH to 7.4 if necessary.
PBS-Tween (0.1% (v/v) Tween 20): 0.5 ml Tween 20 to 500 ml PBS.
PBS-2% (w/v) BSA (Blocker): 10 g BSA to 500 ml PBS, adjust pH to 7.4 with 1 M NaOH. Freeze in 50 ml tubes.
Probing Buffer: 5% (w/v) Carnation Skim Milk Powder in PBS + 0.1% (w/v) Tween 20. Adjust pH to 6.5 with 1 M Phosphoric Acid. Centrifuge at 3500 X g for 30 minutes just before addition of antibody.
Bromophenol Blue: 0.1% (w/v) Bromophenol blue in water.
Amido Black: 100 mg Amido Black, 45 ml Methanol, 10 ml Acetic Acid, 45 ml water.
Destain Solution: 10% (w/v) Acetic Acid, 25% (w/v) Methanol in water.
ECL Western Blotting Detection System: Amersham #RPN-2106
Solutions Required:
A. SDS PAGE:
For precast 10 x 8 cm gels: Prepare samples and load 0.5 ul plasma or 50 ng purified protein per well. Electrophorese until the dye front is at the edge of the gel.
B. Electroblotting onto membrane:
When tracking dye has reached bottom of gel, turn off power supply.
Hydrate membrane (nitrocellulose or Immobilon-P PVDF) as per manufacturer’s instructions. For Immobilon this consists of a 10-second wash in 100% MeOH followed by 60 seconds in distilled water then several minutes in the transfer buffer. The cassette is then assembled with sponge on bottom, followed by 3MM filter paper, gel, membrane, filter paper and top sponge. Each item should be soaked by dipping in transfer buffer prior to assembly of the cassette, and kept wet during the assembly. Do not allow air bubbles to become trapped between the gel and membrane. The cassette is closed and placed in the Transphor unit with the membrane on the cathode side (red) of the gel.
Transfer of proteins is performed at 500 mAmps for 1 hour at RT.
C. Probing and detection:
Turn off power and remove the cassette from the Transphor unit. Trim the membrane to the same size as gel. Put a small nick in the membrane to mark the point of application of the first sample. Cut off molecular weight standard lane and stain in Amido Black for 5 minutes, and then destain. Place remaining membrane in a plastic dish containing 50 ml of PBS-2% (w/v) BSA (blocking solution).
Block membrane for 2 hours at ambient temp., or overnight at 4oC on a shaking platform.
Rinse briefly with PBS-Tween.
Incubate membrane with 50 ml probing buffer containing peroxidase conjugated antibody for 2 hours at ambient temperature on a rocker. The appropriate dilution for each species should be determined by titration.
Wash membrane with PBS-Tween three times, 15 minutes each.
Develop as per instructions for the ECL Western Blotting Detection System, starting at step #12 on page #12 in the ECL Instruction Manual. Exposure times using Kodak XAR-5 film is typically between 2 and 20 minutes at room temperature.
Reference
Towbin, H., Gordon, J.: Immunoblotting and Dot Immunobinding -Current Status and Outlook. J. Immunol. Meth., 72:313 (1984).
Methods for Immunoblotting of von-Willebrand Factor
Immunoblotting of von Willebrand Factor Polymers in Plasma and Platelets using Peroxidase Conjugated Antibody and Chemiluminescence Detection
Principle
Patient platelet-poor-plasma proteins are partially denatured using heat and an anionic detergent, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS). This detergent binds to all plasma proteins. The amount of anion bound to the protein is directly proportional to the size of that protein. Thus, when SDS treated plasma proteins are subjected to an electric current they will migrate towards the positive electrode (anode). If forced to move through an agarose “sieving” medium, smaller proteins will migrate faster than larger proteins, and a size dependent distribution of plasma proteins is the result. After electrophoresis, the proteins are transferred out of the gel onto nitrocellulose membrane. The nitrocellulose is then blocked and probed with a peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-vWF antibody. The vWF bands are then visualized using the Amersham Enhanced Chemilumescent Detection System. Normal polymers of von Willebrand factor range in size from 1 to 14 million Daltons in molecular weight. In some variants of von Willebrand’s disease, the larger polymers are missing from the plasma. The gels of higher concentration agarose (3%) are required if triplet substructure is to be defined, while gels of lower agarose concentration (1.5%) allow more straightforward identification of type II variants.
References:
Budde, U., Schneppenheim, R., Plendl, H., Dent, J., Ruggeri, Z.M., Zimmerman, and T.S.: Luminographic Detection of von Willebrand Factor Multimers in Agarose Gels and on Nitrocellulose Membranes. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 63(2): 312-315, 1990.
Ruggeri, Z. M., Zimmerman, T.S.: Variant von Willebrand’s Disease. Characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of FVIII/vWF in plasma and platelets. J. Clin. Invest., 65:1318, 1980.
Towbin, H., Gordon, J.: Immunoblotting and Dot Immunobinding – Current Status and Outlook. J. Immunol. Meth., 72:313, 1984.
Equipment Required:
Power supply, capable of delivering up to 100 V., O.1 A.
Horizontal slab gel electrophoresis apparatus (LKB Multiphor 2117).
Boiling water bath or Microwave oven.
60oC water bath.
Anticondensation lid, Plexiglas, 110 x 250 x 4 mm.
Gel pouring kit (gel should be poured using a “sandwich” method).
Whatman 3 MM filter paper.
Small (1mL) plastic test tubes with caps.
Container for washing gel, at least 14 x 28 cm.
PVDF membranes (Millipore Corp.) Used as per manufacturers instructions.
Transphor Electroblotting Unit (LKB #2005 or Hoefer #TE62X) or equivalent, complete with power supply, cassettes and sponges.
Materials Required:
Description and Source:
Antibody: Peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-vWF (ABI #GAVWF-HRP)
Tris: Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane. “Trizma Base” Sigma #T-1503
Glycine: Sigma #G-7126
SDS: Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: Pierce #28365 (Note: SDS is a respiratory tract irritant. Weigh without raising dust.)
BSA: Bovine serum albumin RIA Fraction V: Sigma #A-7888
Glacial Acetic Acid: BDH #B10001-78
Agarose: HGT(P) Agarose: FMC Corp.
ECL Western Blotting Detection System: Amersham Pharmacia #RPN-2106
Bromophenol blue: BDH #B20015-20
Preparation:
(Note: use Milli-Q water or comparable purity for all reagents.)
Stacking gel buffer: 0.125 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8
To make 500 ml: 7.57 grams Tris to 500 ml water. pH to 6.8 with HCl. (Note : add SDS to 0.1% (w/v) just before use.)
Separating gel buffer: 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8
To make 1 liter: 45.41 grams Tris to 1 liter water. pH to 8.8 with HCl. (Note: add SDS to 0.1% (w/v) just before use.)
Tray buffer: 0.05 M Tris, 0.384 M Glycine, 2.5 g SDS (0.1% (w/v)), pH 8.35
To make 2.5 liters: 15.0 grams Tris, 72.0 grams Glycine, 2.5 grams SDS, adjust pH to 8.35 if necessary with 1M HCl or 1M NaOH.
Sample prep buffer:
Stock: 0.1 M Tris-HCl, 0.01M EDTA, pH 8.0 Store at 4oC.
To make 100 ml: 1.21 grams Tris, 0.372 g Na2EDTA, pH to 8.0 with HCl.
Working Solution: 0.01 M Tris-HCl, 0.001 M EDTA, 2% (w/v) SDS pH 8.0
For 100 ml: 10 ml stock solution, 90 ml water, add 2.0 grams solid SDS.
PBS: 8.0g NaCl and 1.15g Na2HPO4, 0.2g of KH2PO4, and 0.2g of KCl, up to 1 litre, pH to 7.4.
PBS-2% (w/v) BSA (Blocker): 10 g BSA to 500 ml PBS, readjust pH to 7.4.
Transfer Buffer: To make 6 liters: Add 42.59 g Na2HPO4, 2.4 g SDS, pH to 7.4 with 1 M H3PO4. Store at room temp.
Probing Buffer: 5% (w/v) Carnation Skim Milk Powder in PBS + 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20. Adjust pH to 6.5 with 1 M H3PO4. Centrifuge at 3500 X g for 30 minutes just before addition of antibody.
Bromphenol Blue: 1% (w/v) Bromphenol blue in water.
Collection and Handling of Specimens:
4.5 ml of venous blood is drawn into a plastic syringe and anticoagulated with 3.8% trisodium citrate (4.5 ml blood to 0.5 ml trisodium citrate). Patient must be fasting.
Platelet poor plasma (PPP) is prepared by centrifuging the specimen in table-top centrifuge at 3000 rpm (100 x g) for 10 minutes at room temperature.
PPP is carefully removed with a plastic transfer pipette, placed in a plastic test tube and frozen and stored at -20oC or below.
Sample preparation for platelet vWF multimeric analysis:
Collect blood as above, but spin for 5 min @ 180 X G
Perform platelet count on the PRP and calculate volume required to give total of 2.5×108 platelets.
Spin required volume of PRP in a microfuge for 1 minute to achieve pellet of 2.5×108 platelets.
Save supernatant and freeze (for plasma vWF analysis) and freeze platelet pellet
Thaw pellet and add 900 ul H20.
Freeze & thaw 5 times (to lyse platelets).
Spin in microfuge, 1 min & remove supernatant (contains released vWF)
Add equal volume of 0.5% Triton X-100 (v/v) in 5% SDS (w/v) and incubate for 15 minutes at 60oC.
Spin in microfuge and apply to gel as for plasma. (Note: Can use 1×108 platelets but scale everything down.)
Method
A. Pouring the gel (“sandwich” method):
1. The sandwich or mold consists of two glass plates, a U shaped spacer, 1 mm thick and four clamps.
2. Place 1 mm spacer between the two glass plates. Clamp assembly together and place mold(s) in 60oC oven for 15 minutes.
3. For the separating gel, weigh appropriate amount of agarose (see below) and place in 50 mL glass tube containing 20 ml separating gel buffer. Cap tube to prevent evaporation. Place in boiling water bath or microwave to thoroughly dissolve the agarose. Add 0.2mL 10% SDS. Next place tube in 60oC water bath for at least 10 minutes.
For desired gel, add the following weight agarose to 20 ml separating gel buffer:
1.6% gel: 320 mg agarose (routinely used)
2.0% gel: 400 mg agarose
2.25% gel: 450 mg agarose (best for triplets)
5. Remove mold from oven. Place mold vertically on bench with opening facing up. Pour 20 ml agarose into mold. Do not inject air bubbles. Allow gel to cool to room temperature for a minimum of 40 minutes.
6. Disassemble mold and remove top plate. Cut gel to a length of 8.6 cm. Reassemble gel in mold.
7. Prepare stacking gel (0.8% agarose): place 80 mg agarose in a 40 ml centrifuge tube containing 10 ml stacking gel buffer. Cap tube and place in boiling water bath or microwave. After agarose is melted, cool in a 60oC water bath for a minimum of 10 minutes. Add 0.1mL 10%SDS.
8. Fill the mold with agarose solution using a pre warmed disposable pipette. Reserve an aliquot of stacking gel solution to fill the wells of the gel during electrophoresis (keep at 60oC). Allow gel to cool 40 minutes.
9. Disassemble mold and remove top plate. Cut gel to 12 cm length. Carefully cut five evenly spaced wells, each 2 x 11 mm, and remove agarose by suction. Wells are 1.0 cm from and parallel to the stacking gel separating gel interface.
B. Preparation of the samples:
1. Frozen samples are thawed at 37oC. 25 ul of sample is added to tube containing 70 ul of sample prep buffer and 5 ul of bromophenol blue.
2. Mix diluted sample and place in 60oC water bath for 15 minutes.
C. Preparation of electrophoresis unit and running gel:
1. Place 2.5 liters of tray buffer in beaker. Add 2.5 grams solid SDS. This will dissolve without stirring. After dissolved, stir briefly and adjust pH to 8.35 if necessary using 5 M NaOH. Place 1.2 liters in each of the two reservoirs of electrophoresis unit.
2. Pipette a milliliter or two of tray buffer onto the electrophoresis unit’s glass cooling plate. Place agarose slab (still on bottom glass plate of mold) on cooling plate so that the stacking gel and the wells are on cathode ( ) side. Turn on cooling water. Cooling water should be either running tap water or preferably refrigerated circulation at 10oC. Use five pieces of filter paper on each side as wicks. Dip wicks in tray buffer and place them on gel so that they are parallel to each other. The wicks are placed 10 cm apart.
3. Carefully pipette 14 ul of sample into each well. Install anticondensation lid and electrophoresis unit cover. Current will not flow without the cover installed; also protects operator from shock. Turn power supply on and set to 12 mA/gel for 45 minutes; this moves the plasma proteins from the well into the agarose. Shut off power and remove unit’s cover and anticondensation lid; fill in wells with stacking gel buffer/agarose using a plastic transfer pipette. Turn on power and continue electrophoresis until dye front reaches anodal wick. Electrophorese at 10 mA/gel for 6 hours or 4.5 mA/gel for about 16 hours.
D. Electroblotting onto nitrocellulose membrane:
1. When tracking dye has reached bottom of gel, turn off power supply.
2. The cassette is assembled per manufacturer’s instructions with sponge on bottom, then 3MM filter paper, then gel, nitrocellulose membrane, filter paper and top sponge. Each item should be soaked by dipping in elecroblot buffer prior to assembly of the cassette, and kept wet during the assembly. Do not allow air bubbles to become trapped between the gel and nitrocellulose. The cassette is closed and placed in Transphor unit with the nitrocellulose on the cathode side (red) of the gel.
3. Transfer of protein from the gel to the membrane is performed for 2 hours at 16oC at 500 mAmps.
E. Probing and detection:
1. Turn off power supply. Remove cassette from Transphor unit and trim membrane to the same size as gel. Put a small nick in the membrane to mark the point of application of the first sample. Rinse the membrane briefly in transfer buffer then place in a Tupperware dish containing 50 ml of PBS BSA2% (blocking sol’n).
2. Block membrane for 1 hour at ambient temperature on a platform shaker.
3. Rinse briefly with PBS Tween.
4. Incubate membrane with 50 mL Probing buffer containing peroxidase conjugated antibody (#GAVWF HRP) at approximately 0.2 ug/ml for 1 hour at ambient temperature on a rocker. The optimal antibody concentration should be determined by titration.
5. Wash membrane with PBS Tween three times, 15 minutes each.
6. Develop as per instructions for the ECL Western Blotting Detection System, starting at step #12 on page #12 in the ECL Instruction Manual. Typically a 2 min exposure time is sufficient using Amersham Hyperfilm MP.
Methods for Immunohistochemistry of von-Willebrand Factor
Immunohistochemical Staining for von-Willebrand Factor (vWF) Using Affinity Purified Goat antibody and Vectastain-Elite ABC Kit
Introduction
von Willebrand Factor (vWF) is an adhesive protein that circulates in plasma at about 10 ug/ml and is also found in platelets and endothelial cells. vWF is found as multimers of disulphide-linked 220,000 Dalton subunits and its molecular weight ranges from 0.5-20 million Daltons. vWF is involved in the transport of Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor) and plays an important role in platelet adhesion and aggregation. von Willebrand Disease (vWD) can be due to a quantitative deficiency of vWF (vWD Types I & III) or to qualitative disorders resulting from the production of functionally abnormal protein (vWD Type II). The procedure outlined here was developed for immunohistochemical staining of vWF in endothelial cells at the light microscopy level and uses Product # GAVWF-AP as the primary antibody, Biotinylated rabbit anti-goat IgG (Product # BA-5000, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) as the second antibody. Detection of biotinylated antibody was performed using the VectaStain-Elite detection kit from Vector Labs.
Method
Paraformaldehyde fixed tissues samples were embedded in paraffin.
Remove paraffin in toluene (2 X 20 min).
Put through graded alcohols (100% – 25% (w/v), 5 min each), then rinse in water.
Block with methanol-peroxide (0.3% H2O2 in MeOH) for 30 minutes.
Sections were washed in PBS (10 mM NaHPO4, pH 7.4, 0.15 M NaCl) for 20 min.
Layer on PBS containing a 1/100 dilution of normal rabbit serum for 20 min.
Rinse and layer on the primary antibody diluted in PBS containing 1% (w/v) Bovine Serum Albumin and place in a humidity chamber overnight at 4oC.
Note: For vWF staining we recommend affinity-purified goat anti-vWF (GAVWF-AP) diluted to 0.5 ug/ml. In general, affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies or purified monoclonal antibodies may be used in a concentration range of 0.5 to 5 ug/ml, while whole IgG antibodies or ascites may be used in a concentration range of 5 to 25 ug/ml. Optimal concentrations of each different primary and secondary antibody should always be determined empirically by titration.
Wash in PBS for 10 minutes then layer on secondary antibody (biotinylated Rabbit anti-Goat IgG) diluted approximately 1/100 in PBS for 30 minutes at ambient temperature.
Wash in PBS for 10 minutes, then apply the VectaStain ABC reagent mixture as per the manufacturerÕs instructions.
Develop in 0.05% (w/v) DAB in 0.05 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, containing 0.075% H2O2 for 15 minutes at ambient temperature.
Rinse in cold water, then counterstain in hematoxylin for 3-5 minutes.
Rinse in water, then graded alcohols (25% – 100% (w/v), 5 minutes each).
Rinse in 3 changes of toluene then coverslip with permount.